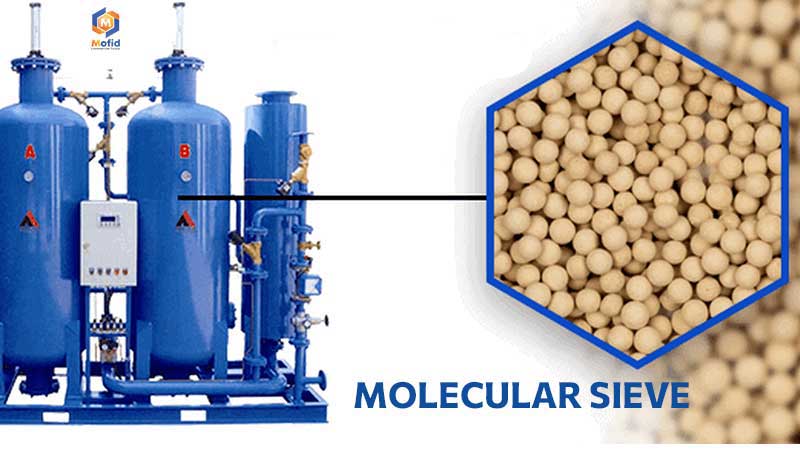
Molecular Sieve
Molecular sieve is a crystalline material from the family of aluminosilicates, characterized by its uniform and extremely fine porosity. This structure allows molecular sieves to precisely and effectively adsorb molecules, particularly water. When heated, the crystal water is removed without damaging the structure, making this reversible property one of the best options for moisture removal from gases and liquids. Compared to older adsorbents like silica gel, molecular sieves offer purer results.
Types of Molecular Sieves
Molecular sieves are classified into different types based on pore size and applications. Four of the most important types of molecular sieves are:
Molecular Sieve 3A
Molecular sieve 3A is a type of adsorbent with pores of 3 angstroms in diameter, specifically designed for the adsorption of small molecules. This adsorbent is especially used in the drying of non-polar gases.
Features of this product:
- Dehydration of CNG
- Dehydration of compressed air
- Dehydration of refrigerant gases such as R134a
- Production of absolute alcohol
- Purification of carbon dioxide gas
Molecular Sieve 4A
Molecular sieve 4A is an adsorbent used for absorbing water and molecules such as methanol, ethanol, and ammonia. The pore size of this material is about 4 angstroms and it has a porous structure.
Features of this product:
- Dehydration of CNG
- Deep dehydration of compressed air
Molecular Sieve 5A
Molecular sieve 5A has pore sizes around 5 angstroms, allowing it to adsorb molecules smaller than 5 angstroms. This material can absorb larger molecules such as nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide, and is used for nitrogen separation from air.
Features of this product:
- Dehydration and sulfur removal from natural gas
- Hydrogen purification
- Carbon dioxide removal
Molecular Sieve 13X
Molecular sieve 13X has pore sizes approximately 10 angstroms (0.1 nanometers), allowing it to adsorb larger molecules like hydrogen sulfide, CO₂, and organic compounds, and is widely used in oil and gas refining.
Features and Applications:
- Oxygen production
- Adsorption and purification of gases and vapors
- Removal of nitrogen from gas mixtures
- Reducing moisture and improving air quality
Types of Molecular Adsorbents
Molecular adsorbents are materials designed for the separation and adsorption of molecules. Due to their porous structure and specific properties, these adsorbents are capable of separating and absorbing molecules. Below are some of the different types of molecular adsorbents:
Zeolites
Zeolites are naturally occurring or synthetic minerals with a crystalline and porous structure. They are used in separation processes, water purification, and as catalysts in chemical industries.
Molecular Sieves
As discussed in this article, molecular sieves are a type of molecular adsorbent. In fact, molecular sieves are also considered a form of synthesized zeolite.
Activated Carbon
Another type of molecular adsorbent, activated carbon has a high surface area and porous structure. It is used to remove pollutants, odors, and toxins from air and water.
Carbon Molecular Sieve
Carbon molecular sieve is a special type of activated carbon used to adsorb specific molecules. It is utilized for the separation of gases and organic substances.
Activated Alumina
Activated alumina also has a porous structure and high adsorption capacity for water and other liquids. It is widely used in separation and purification processes.
Silica Gel
The last molecular adsorbent we will introduce here is silica gel, a silica-based adsorbent primarily used for moisture absorption. It is often used in the packaging of food and pharmaceuticals to control internal moisture.
Purchase Various Types of Molecular Sieves from Mofid Zeolite Trading
All types of molecular sieves and other molecular adsorbents mentioned in this article are available for order through Mofid Zeolite Trading. For more information, please contact the following numbers:
- Tehran Office: 021-28420163
- Semnan Office: 023-33335234
- Sales Manager: 09120697642
- Email: info@zeolitea.com